As part of an ongoing series, members of Flad's science and technology team share their insights on the future of the scientific workplace.
The Hypothesis:
conversations on scientific
research environments
Accelerating Clinical Therapy with GxP Facilities
As part of an ongoing series, members of Flad's science and technology team share their insights on the future of the scientific workplace.
The Mayo Clinic recently engaged Flad to design a unique biomanufacturing space for their Center for Regenerative Biotherapeutics, a groundbreaking facility in Rochester, Minnesota that is speeding up the development and production of life-saving treatments. The new facility has the capability to develop patient therapies and translate them to FDA-regulated manufacturing, all at the same location. Leveraging Mayo Clinic's strong research capabilities, the facility houses process development, GxP, and quality control space. These three core spaces are designed to support the development and scale-up of regenerative treatments and therapies for early-phase clinical trials. This creates a critical pathway connecting patients who may have run out of treatment options to life-saving treatment with a novel, cutting-edge biotherapy.
For example, recently, process development work at this site led to a bio-manufactured and QC-tested solution to fight cancer cells. Instead of the disease progressing, immune-enabled designer drugs were able to not only stop cancer, but more importantly, continually prevent it from returning by activating the patient's natural immune system. This treatment has led to an exciting, life-changing outcome.
These biological therapies and personalized medicine have opened a new world of possibilities to treat diseases. Derived from materials such as the cells, tissues, and genes of living organisms, biotherapies offer the potential for more targeted treatment with fewer side effects than traditional medicine.
A leader in developing and manufacturing biotherapies, Mayo Clinic worked with Flad to design the new Biomanufacturing Facility to be agile, flexible, and adaptable. Driven by rapid innovation and the urgency to translate research into clinical solutions, the space was designed to support diverse research, integrate evolving technologies, and foster interdisciplinary collaboration.

Mayo Clinic worked with Flad to design the new Biomanufacturing Facility to be agile, flexible, and adaptable.
To meet regulatory and operational needs, the project team embedded a GxP-compliant space within the new facility, enabling faster, more efficient biotherapeutic development. While the process for obtaining FDA approval to manufacture drugs for human use under current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) standards is important, it is also lengthy. GxP-compliant process development facilities can accelerate the timeline for clinical therapies to reach patients by helping to improve efficiency for research, development, and manufacture.
GxP Process Development Facilities and Benefits GxP refers to good practices, a set of quality guidelines, and regulations used in the life science industry to ensure products are safe, meet their intended use, and comply with regulatory standards. The x in GxP represents a variety of processes, including current good manufacturing practices (cGMP), good lab practices (GLP), and good clinical practices (GCP). A GxP-compliant operating environment merges these capabilities into a highly flexible unit of operation to enable and support a wide range of campaign needs.
Providing a controlled and documented baseline for regulatory compliance significantly streamlines the scale-up of process development projects and facilitates adaptation to diverse project initiatives. This can be useful for organizations moving from research to clinical-scale or pilot-scale development, when there is not yet a need for a fully integrated clinical- or commercial-scale cGMP-compliant facility. Establishing a GxP-compliant processing facility delivers many of the core capabilities of a cGMP facility, while offering the advantages of a more scalable footprint and reduced complexity in upfront laboratory planning and process architecture design.
With extensive experience supporting major pharmaceutical manufacturing companies in the design of cGMP environments, Flad understands how GxP facilities must be managed and operated to comply with regulatory standards. This includes FDA regulations, guidelines from the European Union (EU) and the International Council for Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), as well as other international standards. By embedding regulatory standards into operational practices, a GxP-compliant facility also enhances efficiency while maintaining quality assurance through consistent regulatory compliance.

A GxP-compliant facility also enhances efficiency while maintaining quality assurance through consistent regulatory compliance.

Breakthroughs and Market Demands that Led to GxP Processing Facilities The concept of GxP has been around for decades. It was developed from the guidelines of cGMP, which represented the FDA's first formalized quality standard in regulating the pharmaceutical and food production industries when they were established in the 1960s in response to public health crises.
Over the past two decades, the pharmaceutical and life science industries have experienced significant growth driven by many factors, including a growing and aging population and more accurate diagnoses of chronic diseases. Scientific breakthroughs leading to advancements in areas such as cell and gene therapy, biologics, theranostics, and personalized medicine have helped to address these growing demands. Personalized medicine, for example, requires moving from research to process development to drug product manufacture, though on a smaller scale compared to a commercial drug product.
Given that most of the Center for Regenerative Biotherapeutics' applications are for patients facing severe medical challenges, often after other treatments have not worked for them, one of the main project goals was to establish a space to efficiently support a diverse portfolio of process development projects. Development projects come in waves, with up to six active projects at any given time, each one lasting anywhere from several months to as long as two years. With six additional projects queued and over 100 in the pipeline, the facility experiences continuous turnover. The flexibility of the GxP space allows these process development projects to scale up to clinical trials and deliver biotherapeutic products to patients who need them the most.
Considerations for Designing a GxP Space The focus of a GxP-compliant space is to ensure quality, consistency, and safety and to guarantee that any products manufactured are safe and effective. Therefore, early planning efforts should consider all aspects of the potential processes required to support regulatory compliance, including operational efficiency, environmental controls, and equipment integration. The planning phase should examine and optimize process flows, including personnel, materials, products, and waste, while also reviewing adjacencies and other Lean operational strategies.
Additionally, the Center for Regenerative Biotherapeutics project consolidated its QC operations by incorporating an on-site QC lab. The QC lab supports the new biomanufacturing facility, as well as other facilities across Mayo Clinic's biomanufacturing enterprise. Its strategic collocation with the Process Development Lab minimizes sample handling and transport, enhancing oversight and improving turnaround times. This streamlined workflow accelerates the development of regenerative therapies and supports their readiness for clinical application. This is a distinctive feature that enabled Mayo Clinic to conduct in-process testing without leaving the facility.
Lastly, an important consideration for the Center for Regenerative Biotherapeutics was the need for space to train staff in aseptic techniques and GMP-compliant cleaning protocols. A smaller scale operation that can meet cGMP compliance creates a perfect sandbox for training without disrupting cGMP operations at active processing facilities.
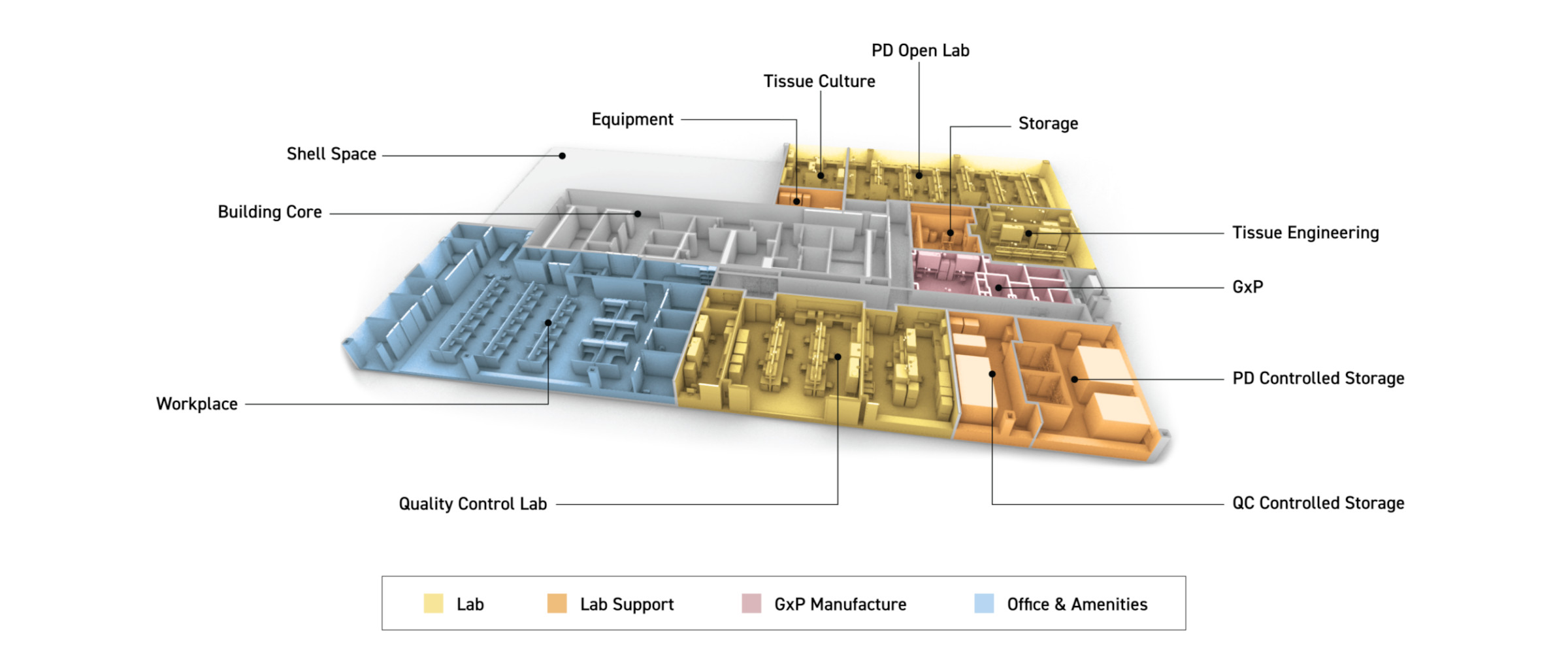
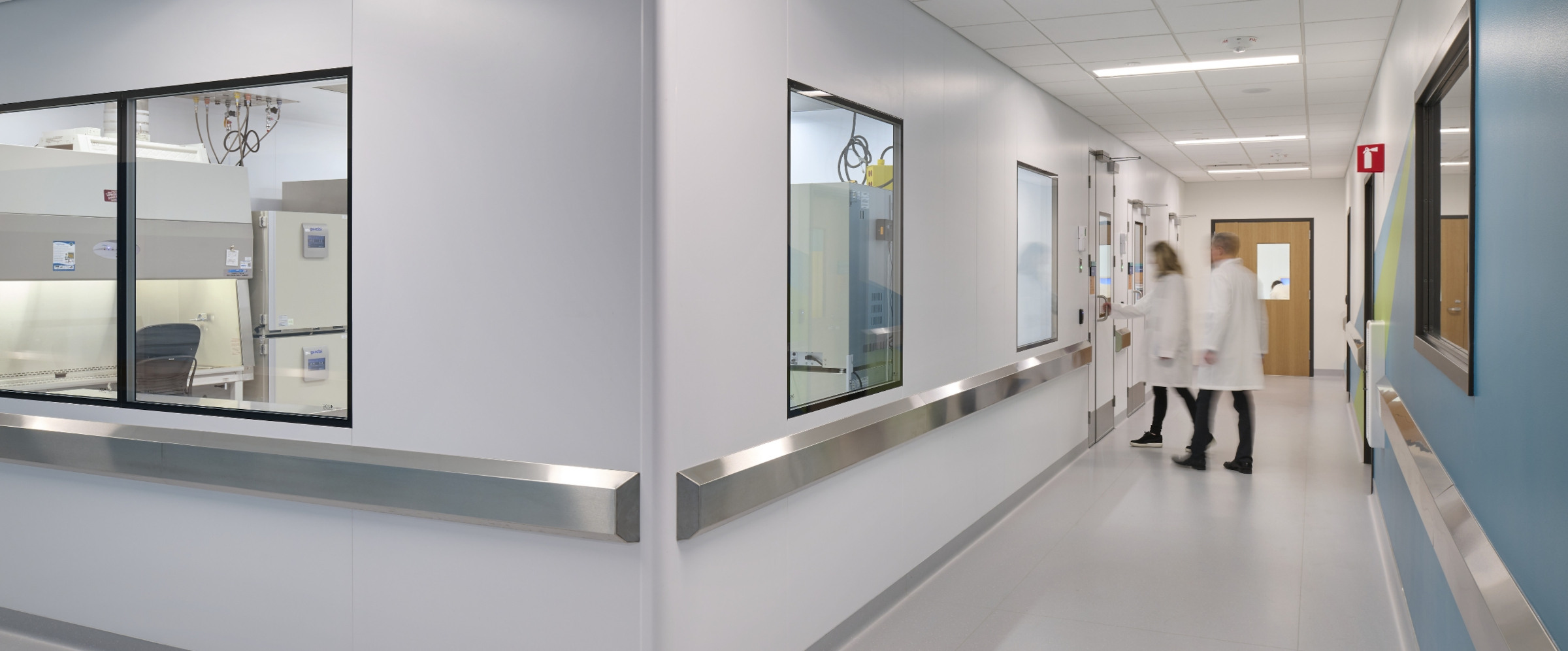
Importance of Adjacencies and Flexibility In alignment with intentional adjacencies, the design incorporates internal visual connections to provide clear sightlines into the lab spaces, fostering a sense of unity across distinct lab areas and enhancing a collaborative atmosphere. This transparency contributes to overall well-being and creates a more welcoming environment for staff as well as tours with potential Mayo Clinic partners.
Beyond design considerations for a GxP-compliant space, location and adjacencies play a critical role in operational workflows, particularly in efficient sample movement and supporting a range of interconnected processes. The Center for Regenerative Biotherapeutics headquarters is strategically located near Mayo Clinic's downtown Rochester hospital campus. It sits within the Discovery Square Campus, which is dedicated to bioscience. Mayo Clinic also operates a manufacturing facility in a building directly adjacent to the Center for Regenerative Biotherapies and another location directly downtown.
A significant goal of the project was to provide maximum flexibility. Leveraging our experience planning and designing a wide range of biotech facilities, the design includes elements such as reconfigurable mobile furnishings and ceiling utility panels pre-designed with the infrastructure for future needs, as well as considerations such as airlocks and gowning requirements. The Mayo Clinic GxP lab was designed and built for 70 air changes per hour. This high rate offers flexibility to support initiatives with strict requirements within that space.
Integrating this GxP-compliant space into the project has been crucial to eliminate bottlenecks and speed up delivery of groundbreaking treatment to patients, supporting Mayo Clinic's patient-first mission.
Share your thoughts or questions on these topics or others you'd like to hear our experts address. Email us